How does the cervical spine work?
Why does neck pain occur?
26% and 40% of men and women over the age of 30 have experienced neck pain in the past month, with 5% of men and 7% of women feeling this way all the time.
cervical osteochondrosis
- Difficulty breathing,
- persistent weakness
- unable to breathe fully,
- Pain and burning sensation behind the breastbone,
- Episodes of rapid heartbeat.
Conditions with neck pain
cervical spondylosis

other reasons

Causes of degenerative changes in the cervical spine
- Chronic bedridden condition is a condition in which a person is forced to lie down for more than a month due to an underlying medical condition. As a result, the muscles become weaker - during verticalization, when the load on the muscles increases, they become overly tight. Pain occurs.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases stress on spinal structures and can lead to pain.
- Autoimmune diseases in which cartilage tissue is destroyed (autoimmune arthritis, polychondritis) can also cause neck pain.
Stages of cervical spine degenerative changes
- Phase I: Thinning of the intervertebral discs and slight discomfort in the neck;
- second stage: The intervertebral disc is deformed and the distance between the vertebrae is reduced. Pain worsens with movement of the cervical spine;
- The third phase: Cartilage and vertebrae rub against each other, resulting in persistent neck pain and limited movement. When the cervical spine is severely deformed, vertebral artery syndrome may occur, accompanied by visual and vestibular disorders and headaches;
- Stage 4: Degenerative changes are obvious, and cervical spine movement is very limited and painful. The neck area can be almost completely immobilized.
Symptoms of degenerative changes in the cervical spine
- Neck pain that worsens with movement or standing;
- Pain radiating to the shoulder or arm;
- Numbness, tingling, and weakness in the arms and hands;
- Clicking or grinding sounds in your neck (especially when you turn your head);
- Headache;
- Dizziness attacks;
- Impaired motor coordination;
- Loss of bladder or bowel control.
If such symptoms occur, a neurologist should be consulted as soon as possible.
Symptom types of "cervical osteochondrosis"
- Neck creaking when moving;
- Can not move;
- Violates the relative position of the vertebrae in the neck;
- Smoothing the natural lordosis or lateral curvature of the cervical spine (only seen on X-ray, MRI or CT).
- Numbness of the fingers on one or both hands;
- Burning pain in the neck that radiates to the arm or arms;
- Neck and arm muscle dystrophy.
- Paroxysmal dizziness until loss of consciousness;
- sudden increase in blood pressure;
- noise in ears;
- Blurred vision or spots in the eyes;
- Loss of balance and nausea when moving the head;
- Headache (severe pain on one or both sides).
Diagnosis of degenerative changes in the cervical spine
Diagnosis and treatment of cervical osteochondrosis are performed by a neurologist.
examine
laboratory diagnosis
Instrument diagnostics
- Radiography.Using X-rays, you can identify bone deformations, malignant tumors, and degenerative changes in joints.
- Computer and magnetic resonance imagingTests are performed if lesions in the spine, spinal cord, or brain are suspected. Computed tomography scan revealed vertebral hemangiomas and severe deformity of the cervical spine. Magnetic resonance imaging provides additional information for visualization of muscles, roots, and spinal cord.
- Neuroelectromyography- A method of studying the efficiency of impulse transmission along nerve fibers using low-intensity electric currents. The test can be a little uncomfortable. The research helps elucidate the conduction of impulses along roots, nerves, and from nerves to muscles, confirm nerve or muscle damage, and elucidate the nature and extent of the damage.
Treatment of degenerative changes in the cervical spine

Drug treatment of degenerative changes in the cervical spine
- local anesthetic creams, gels and patches;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Hormone medications are injected into the affected joint area in the form of tablets or injections;
- Muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms;
- Antidepressants can relieve chronic pain.
Non-pharmacological treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Your doctor may recommend a pad or roller with metal or plastic needles. Use 15-30 minutes before bed to relax muscles.
Surgical treatment of cervical degenerative diseases
Complications and consequences of degenerative changes in the cervical spine
- Intractable pain syndrome in the head, neck, and chest;
- Cramps, dyskinesia, and numbness in the hands;
- Frequent dizziness, impaired motor coordination, and fine and gross motor skills.
Prevention of degenerative changes in the cervical spine ("cervical osteochondrosis")

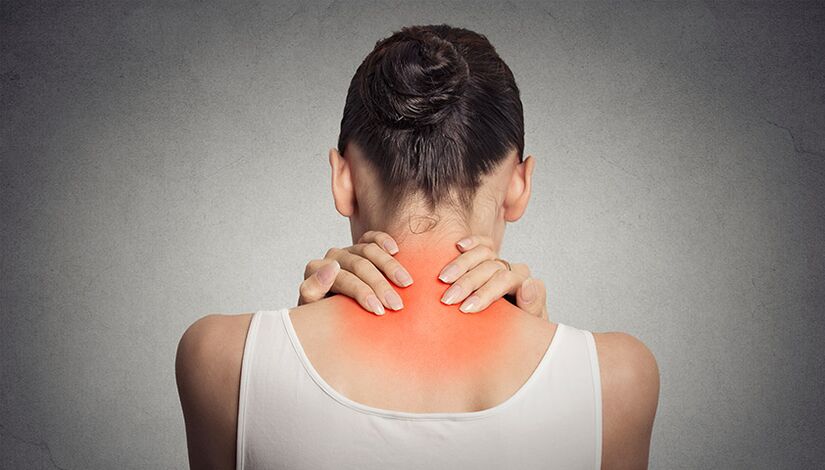
Sleeping positions to relieve back pain
FAQ
- Where does the pain of "cervical osteochondrosis" radiate?
Pain caused by degenerative changes in the cervical spine can radiate to the shoulders or arms and can also worsen with movement or standing. - How to relieve dizziness attacks in "cervical osteochondrosis"?
To relieve dizziness attacks, you should assume a comfortable position that minimizes the possibility of falling (sitting in a chair with a backrest or lying down) and seek help. After 5-7 minutes, you can try turning your head: during this time the onset of dizziness will most likely pass. If dizziness persists or worsens, nausea, vomiting, or other neurological symptoms (impaired speech, vision, movement, swallowing, sensitivity) occur, call an ambulance as soon as possible. - How to sleep correctly with "cervical osteochondrosis"?
When sleeping, the head and spine should be roughly at the same level. This position minimizes additional stress on the neck. - How long will the deterioration of cervical spine "osteochondrosis" last?
On average, worsening of symptoms caused by degenerative changes in the cervical spine ("cervical osteochondrosis") lasts 4 to 7 days. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants are used to reduce pain. During this time, it is best for the person to remain calm and wear a neck brace. - Which doctor treats cervical spine "osteochondrosis"?
Diagnosis and treatment of neck pain are performed by neurologists, neurosurgeons, orthopedists and general practitioners.